PI-RADS for MRI
Overview
To improve early diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer, the American College of Radiology (ACR), the AdMeTech Foundation and European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) formed a joint effort to develop standards for the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS). The goal was to expedite the transfer of high-quality MRI from laboratories to patients to address the major need in prostate cancer care, reducing unnecessary biopsies and treatment.
In this scoring system every parameter: T2WI, DWI, DCE-MRI and MRSI (optional) is scored on a five-point scale. Additionally, each lesion is given an overall score, to predict its chance of being a clinically significant cancer, the scoring should include as a minimum requirement division of the prostate 16 regions, as an optimal requirement into 27 regions.
It has been reported good to moderate inter-reader agreement for the PI-RADS score. In the study by Schimmöller et al., PI-RADS showed high sensitivity and negative predictive value for biopsied lesions. Roethke et al., evaluated the PI-RADS for detection of prostate cancer in patients with magnetic resonance/transrectal ultrasound fusion-guided biopsy, they concluded the system is beneficial to indicate the likelihood of cancer and it is also valuable to identify locations to be targeted with biopsy.
Online Tool
BIOPROGNOS is implementing ―for training or educational purposes―, the last versions of PI-RADS for Prostate Cancer screening and detection. Use will be free of charge and not limited.
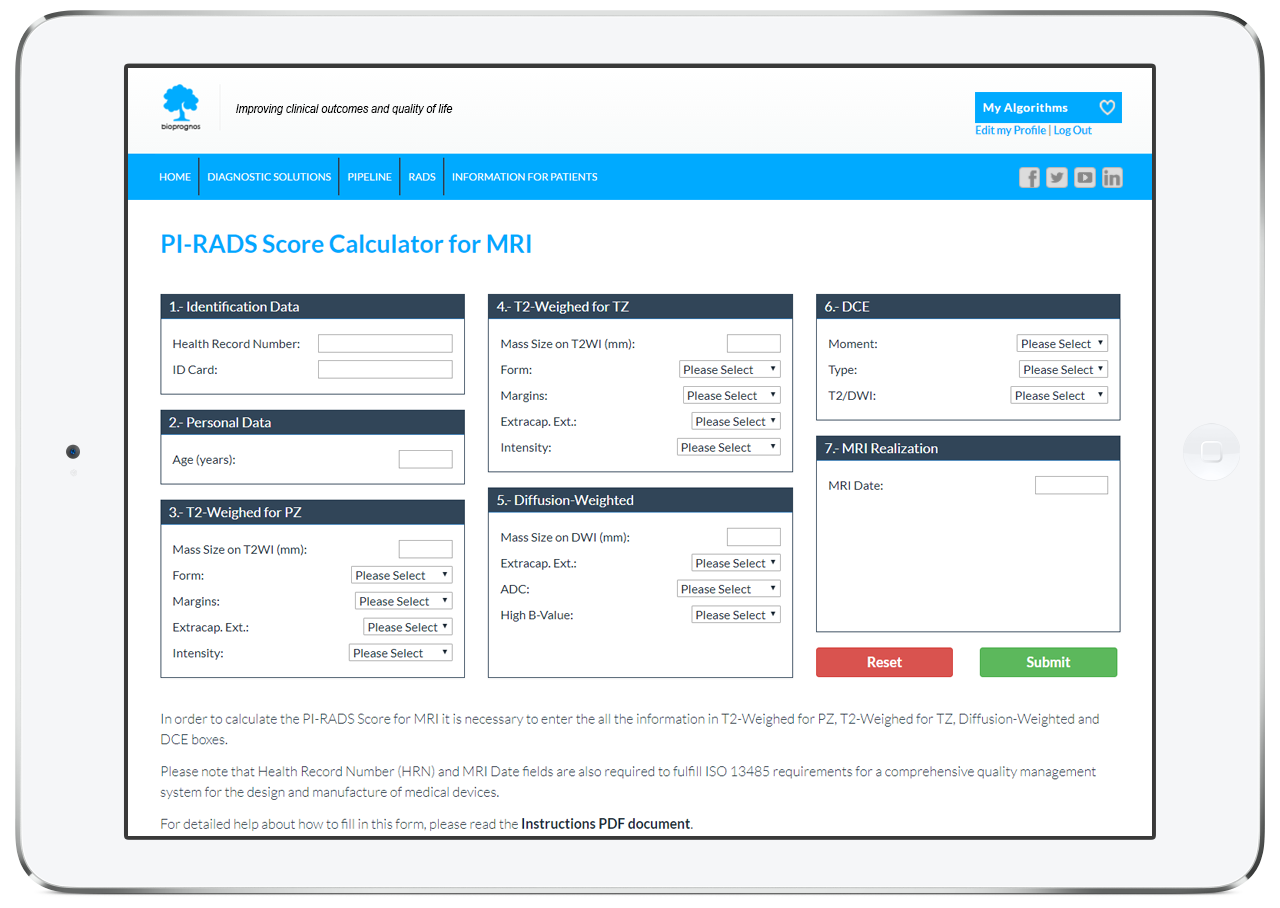
Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) Version 2 by PI-RADS is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Final Report
Once entered the patient data, our PI-RADS Score Calculator for MRI presents the results as a PDF document, that can be downloaded or sent by email.

Click here to open it in PDF format.
The report includes all Patient Data as well as Score, calculated according last version of PI-RADS.
The Science Behind PI-RADS for MRI
Based on Publications
- ACR (2015). PI-RADS Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System. Version 2. American College of Radiology. PDF.
Related Publications
- Barret, T., Turkbey, B., et al. (2015). PI-RADS version 2: what you need to know. Clinical Radiology, 70: 1165-1176. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2015.06.093.
- Rosenkrantz, A. B., Ginocchio L. A., et al. (2016). Interobserver reproducibility of the PI-RADS Version 2 lexicon: A Multicenter Study of Six Experienced Prostate Radiologists. Radiology, 000: 1-12. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2016152542.
- Röthke, M., Blondin, D., et al. (2013). PI-RADS Classification: Structured Reporting for MRI of the Prostate. Clinical Men’s Health. DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1330270.
- Turkbey, B., Choyke, P. L. (2015). PIRADS 2.0: what is new?. Turkish Society of Radiology. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, 21: 382-384. DOI: 10.5152/dir.2015.15099.
- Weinreb, J. C., Barentsz, J. O., et al. (2015). PI-RADS Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. European Association of Urology. European Urology, 69: 16-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.08.052.

